The Federal Reserve (Fed) is widely expected to keep interest rates steady on Wednesday for the third consecutive meeting. This is despite US President Donald Trump’s repeated comments that rates in the United States are too high and should be lowered.
Every time the Fed decides on rates, it is a crucial event as it directly affects families and businesses in the United States.
The interest is the price to pay when borrowing money: personal loans, business loans, student loans, credit cards, mortgages,… the amount of interest in all these ultimately depends on the level of the federal funds rate that the Fed sets.
The Fed decides the level of interest rates independently, meaning that its decisions aren’t subject to approval by the US federal government. Setting interest rates is one of the central bank’s most powerful tools as it directly affects the economy: high interest rates can make borrowing money more expensive for households and businesses, while lower rates can make it cheaper and easier to get a loan approved. This is why Trump wants rates to go down.
What does a rate cut mean and why is it important?
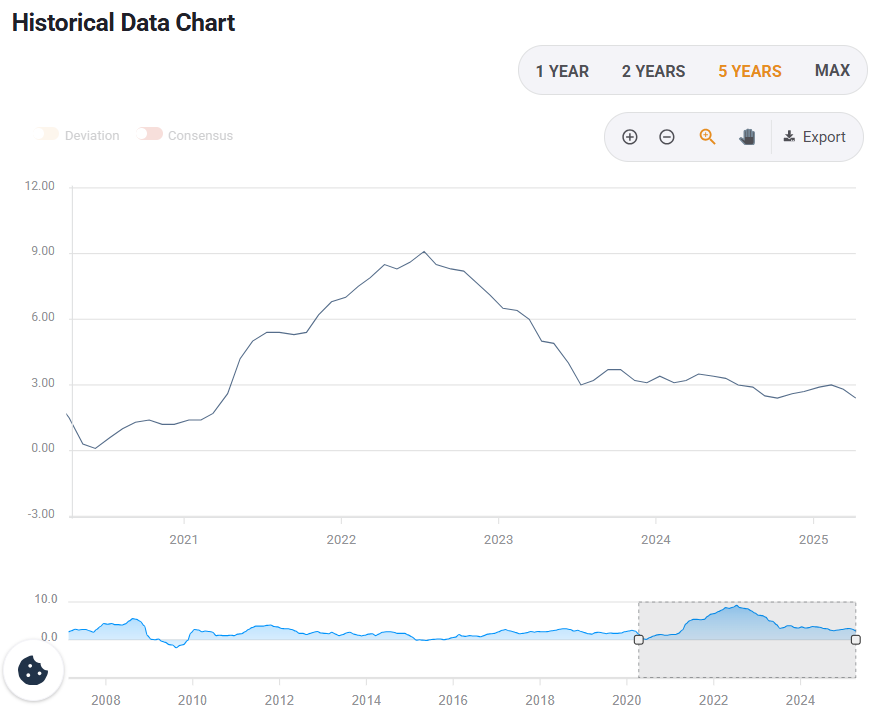
A cut in interest rates means that the Fed reduces borrowing costs. The US central bank opted to lower rates three times in 2024, signaling that the continuous increases seen in 2022 and 2023 were over.
However, rates haven’t been touched since December.
Evolution of interest rates in the United States in the last five years. Source: FXStreet.
But why is this important?
As the rate level set by the Fed basically influences the amount of interest in any loan, lower rates mean consumers and firms will be able to take loans at a cheaper price than before.
So, good news for your pocket.
Now, think big. Lower rates can encourage thousands of people to take a loan to buy big-ticket items and pay less interest for it (and thus be able to spend this money somewhere else). The same applies to businesses, which can get cheaper funds to invest in expansion. This is why lower rates tend to help the economy grow.
Will the Fed cut interest rates on Wednesday?
No, it won’t. Economists and analysts who closely follow the Fed consider that the central bank will opt to keep rates stable again.
As of May 6, 30-day Fed Funds futures prices suggest an almost 96% probability that the Fed will keep rates steady on Wednesday, according to data from the CME FedWatch tool. Only 4.4% expect the US central bank to lower interest rates.
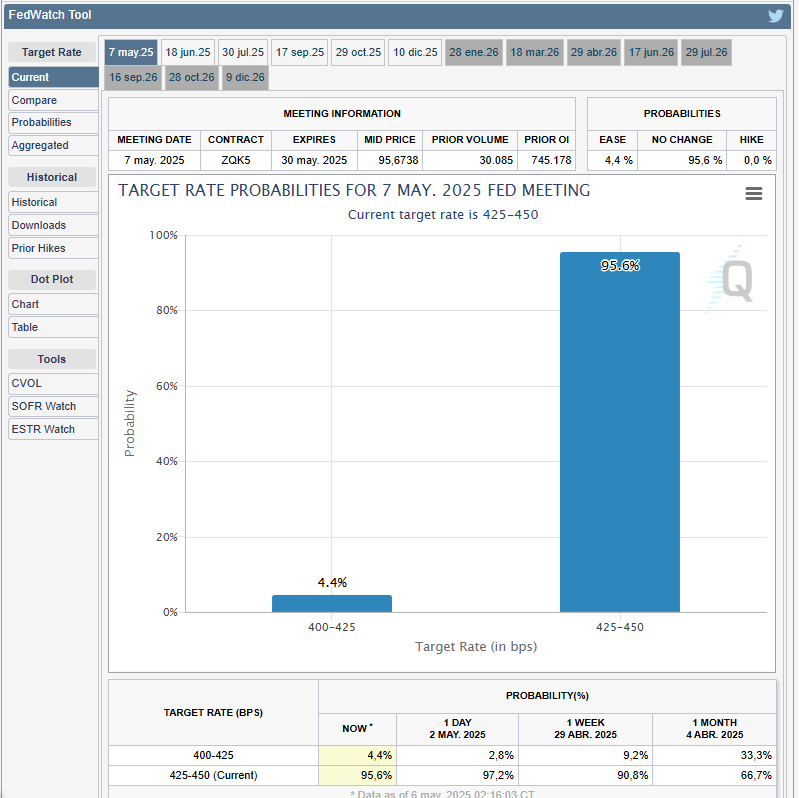
Market pricing of Fed target rate probabilities for May. Source: CME Group FedWatch tool.
Several members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) – the group of people in charge of deciding on interest rates – have signaled a desire to hold rates steady given the increasing uncertainty over inflation and the performance of the US economy.
“I don’t think you should ever take anything off the table – that’s [rate] increases, cuts, holding the same – but the circumstance that we’re in now, where there are a lot of major question marks, is more like we need to wait-and-see how these things are getting resolved,” Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago President Austan Goolsbee said ahead of the decision, Reuters reports. Goolsbee is one of the officials who votes on rates.
What does the Fed look at to decide on rates?
As the US central bank, the Fed has a dual mandate: to promote maximum employment and stable prices.
Since 2022, the inflation rout seen in the US, or the quick rise in prices due to the post-pandemic re-opening, led the Fed to act swiftly because one of its mandates – price stability – was at risk. With prices rising sharply, the central bank decided to quickly lift interest rates with the aim to cool down the economy and keep price rises at bay.
Price increases peaked at 9.1% YoY in June 2022, according to the Consumer Price Index (CPI). Since then, the inflation rate has gradually declined and stood at 2.4% in March, close to the Fed’s 2% target.
Evolution of annual inflation in the United States since 2020, measured by the CPI. Source: FXStreet.
With price increases in the US more controlled, the Fed’s worries about inflation are broadly fading. By itself, this reason would already be enough to reduce interest rates.
The other mandate, which is to preserve employment, also seems to be holding well.
The US labor market has been cooling in the last couple of years, but the most recent data suggests that the economy is still adding jobs at a quite healthy pace and that unemployment levels are under control.
So, what is preventing the Fed from cutting interest rates further?
Uncertainty.
US President Donald Trump’s aggressive tariff policy is keeping Fed officials in a wait-and-see mode.
The high level of tariff imposed – unless trade deals happen soon – could have an effect on prices and the US economy that the Fed doesn’t like: more inflation due to the higher costs of imported goods and, if this persists, even cracks in the labor market.
Minneapolis Federal Reserve Bank President Neel Kashkari said on April 24 that the extreme uncertainty over US trade policy has him “nervous” about big layoffs.
“The Fed remains comfortable waiting to assess the comprehensive impact of pending policy shifts before making further adjustments to the federal funds rate,” said economists at Wells Fargo.
What to look at on Wednesday’s Fed meeting?
With markets fully expecting the Fed to keep interest rates on hold, the focus will be on what the central bank’s statement says and Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s words after the meeting when he speaks to the media.
“Fed Chair Jerome Powell will likely cling to his ‘wait-and-see’ approach due to the current ‘unusual uncertainty’,” says Yohay Elam, senior analyst at FXStreet, in the Orange Juice newsletter.
“While Powell will likely refrain from any commitments, he may pour cold water on hopes for a cut – at least while the economic data remains upbeat (..) I expect Stocks to fall and the US Dollar to rise if Powell refrains from giving any rate cut hopes,” Elam added.
What will the Fed do in next meetings?
It’s unclear.
Fed officials repeatedly say that the central bank is “data-dependent”, meaning that any action in the future will depend on data collected about the state of the US economy.
Usually, the Fed keeps an eye on data related to both inflation and the labor market. If there is increasing evidence that inflation accelerates, this could mean that the Fed could suggest that it will become even more cautious about lowering interest rates.
However, if the economy deteriorates and the labor market suffers, the Fed could opt to cut rates.
“Rate cuts are expected at some point this year, though Chair Powell has consistently emphasized the Fed’s commitment to returning inflation to its 2% target and would not hesitate to raise rates again if inflation pressures reaccelerate,” economists at Wells Fargo say.
However, “as [economic] growth likely weakens and the unemployment rate moves higher as the year rolls along, we look for the FOMC to restart its easing cycle,” they add.
(This story was corrected on May 7 at 07:10 GMT to say, in the first paragraph, that the Fed is expected to hold interest rates steady for a third consecutive meeting, not a fourth.)
Economic Indicator
Fed Interest Rate Decision
The Federal Reserve (Fed) deliberates on monetary policy and makes a decision on interest rates at eight pre-scheduled meetings per year. It has two mandates: to keep inflation at 2%, and to maintain full employment. Its main tool for achieving this is by setting interest rates – both at which it lends to banks and banks lend to each other. If it decides to hike rates, the US Dollar (USD) tends to strengthen as it attracts more foreign capital inflows. If it cuts rates, it tends to weaken the USD as capital drains out to countries offering higher returns. If rates are left unchanged, attention turns to the tone of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) statement, and whether it is hawkish (expectant of higher future interest rates), or dovish (expectant of lower future rates).
Read more.
Next release:
Wed May 07, 2025 18:00
Frequency:
Irregular
Consensus:
4.5%
Previous:
4.5%
Source:
Federal Reserve

